Maternal Screening

Maternal screening tests are crucial for assessing the risk of chromosomal abnormalities and certain fetal conditions during pregnancy. These tests include Dual Marker, Triple Marker, and Quadruple Marker tests, which analyze specific biochemical markers in maternal blood to estimate the probability of conditions such as Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18), and neural tube defects (NTDs).
Maternal screening tests provide non-invasive, early risk assessment for fetal abnormalities, helping clinicians guide further diagnostic testing (e.g., NIPT, amniocentesis) if necessary. Our advanced equipment, FMF-certified software, and expert interpretation ensure accurate and timely results for optimal prenatal care.
Maternal screening involves a series of non-invasive tests performed during pregnancy to assess the risk of certain conditions or birth defects in the fetus. These tests help in early detection, allowing parents and healthcare providers to make informed decisions for better prenatal care.
Maternal screening plays a crucial role in modern prenatal care, offering expectant parents valuable insights into their baby's development. By identifying potential health risks early, these tests enable timely medical intervention and informed decision-making. While not diagnostic, maternal screening provides an essential first step in evaluating fetal health, giving parents peace of mind.

Dual Marker Test (First Trimester Screening - FTS)
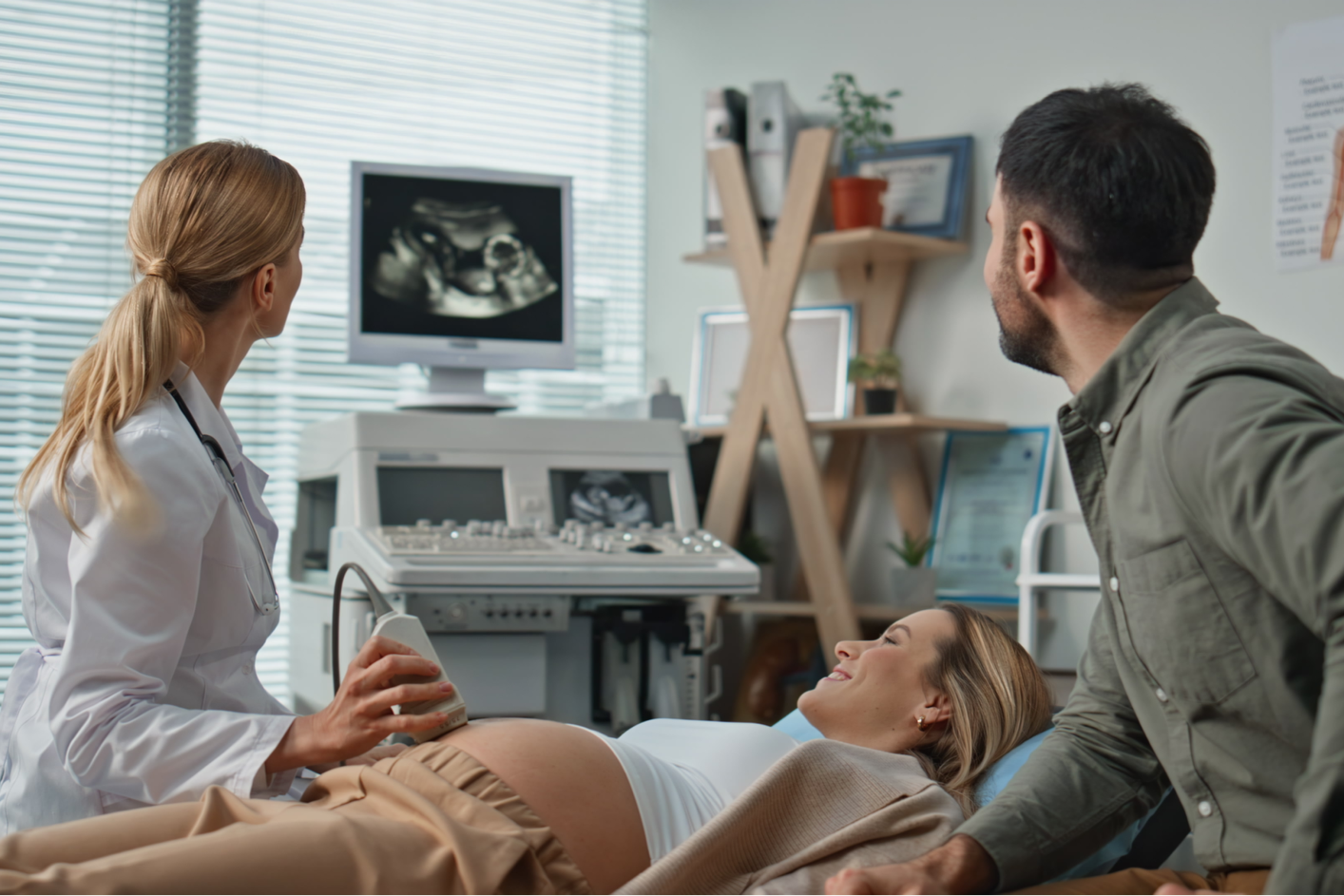

- Free Beta-hCG (β-hCG): Elevated levels indicate a higher risk of Down syndrome.
- Pregnancy-Associated Plasma Protein-A (PAPP-A): Lower levels are linked to chromosomal abnormalities.
- Ultrasound Parameter: Nuchal translucency (NT) measurement is combined with biochemical markers for a more accurate risk assessment.
Triple Marker Test (Second Trimester Screening - TMS)



- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP): Elevated levels suggest neural tube defects; lower levels are linked to Down syndrome.
- Unconjugated Estriol (uE3): Lower levels indicate potential chromosomal anomalies.
- Beta-hCG: High levels suggest increased risk of Down syndrome.
- Clinical Utility: Assesses risks of Down syndrome, Trisomy 18, and neural tube defects.

Quadruple Marker Test (Advanced Second Trimester Screening - QMS)

- AFP, uE3, and β-hCG (as in the Triple Marker test)
- Inhibin-A: Higher levels are associated with Down syndrome.
- Clinical Utility: More accurate than the triple test for Down syndrome risk assessment.
Technology & Data
Interpretation





